What Are the Different Grades of Metamorphism Explain Differences
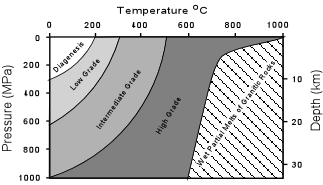
Metamorphism Occurs Between Diagenesis And Melting. Metamorphic grade is a general term for describing the relative temperature and pressure conditions under which metamorphic rocks form.
Metamorphic Rocks Minerals Grade And Facies Lucky Sci
Regional metamorphism works by compressing rock which can often cause the rock to be layered or foliated.
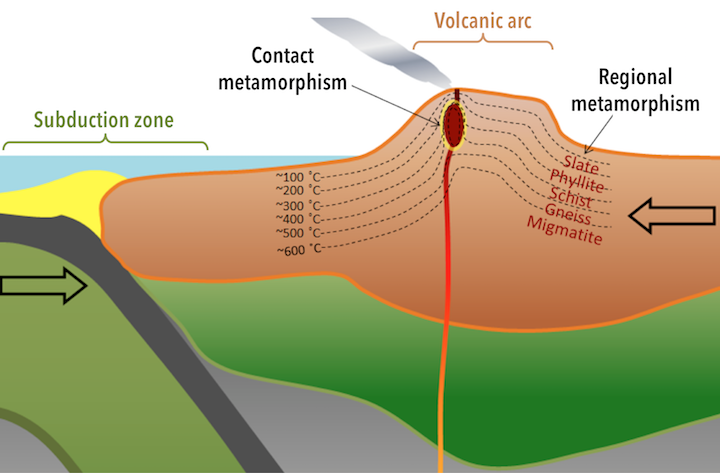
. These rocks were typically exposed to tectonic forces and associated high pressures and temperatures. Contact processes work by raising the local temperature and producing hornfels. How are these differences reflected in the minerals formed during metamorphism.
Progresses incrementally degrees of metamorphism exhibited by changes in rock texture and mineralogy low grade. Regional metamorphism is the creation of metamorphic rock from large geographically significant processes like plate tectonics. Metamorphic grade refers to degree or state of metamorphism.
Meta after morph form so metamorphism means the after form. Answer 1 of 2. What are three different grades of metamorphism and explain how all three grades are formed.
Explain When limestone is metamorphosed there is little. Each type of metamorphism generates distinct rock types. Using this concept grade and index minerals a walk across Scotland becomes a walk through different metamorphic conditions.
Hornfels is a fine-grained rock that shows no signs of layering. What are the differences between magmatism volcanism and metamorphism. Metamorphic grades is a general term for describing the relative P-T condition under which the metamorphic rocks from.
There are two major ways of forming a metamorphic rock. GRADE OF METAMORPHISM Low-grade metamorphism It takes place at temperatures between about 200 to 320oC and relatively low pressureLow grade metamorphic rocks are characterized by an abundance of hydrous. Some types of metamorphism are characteristic of specific plate tectonic settings but others are not.
Metamorphic grade is a general term for describing the relative temperature and pressure conditions under which metamorphic rocks form. Since they were muds and sandstones there have been some. Compare the mineral groups that you would expect to form from intermediate-grade metamorphism of shale basalt and limestone.
Answer 1 of 4. Module 4 Metamorphic Processes and Products Temperature pressure and metamorphism Key definition. This is a type of metamorphism where rock minerals and texture are changed by heat and pressure over a wide area.
As the temperature andor pressure increases on a body of rock we say the rock undergoes prograde metamorphism or that the grade of metamorphism increases. The major difference between these two types of rock is that biochemical rock has once living fossilized organisms in it. The word Metamorphism comes from the Greek.
Most retrogressive events are probably just a. Describe the major compositional differences between shale and basalt. Caused by intense local stresses which break up rocks sometimes reducing them to a fine powder.
In geology this refers to the changes in mineral assemblage and texture that result from subjecting a rock to pressures and temperatures different from those under which the rock originally formed. New metamorphic rocks can form from old ones as pressure and temperature progressively increase. With rocks its metamorphism.
This fact has given birth to the concept of Metamorphic Zones that signify the range of metamorphic effects at different depths below the surface. Metamorphism is a process of mineral assemblage and texture variation that results from the physical-chemical changes of solid rocks caused by factors such as crust movement magma activity or thermal fluid change in the earth. Shale becomes more compact.
The lowest facies of metamorphism is generally considered the zeolit. Other than that they are virtually similar in every aspect. Magmatism is the production and migration of magma which is molten rocks produced from the partial melting of solid materials within a planetary body.
Contact metamorphism is the creation of metamorphic rock from the. The parent rock or protolith is the rock that exists before metamorphism starts. It is a different story for our second type of metamorphism.
Know that the metamorphic grade is determined by the temperature and pressure at which rocks are metamorphosed. This method produces mylonite. 4 min read.
The main difference between contact and regional metamorphism is that contact metamorphism occurs in a small region whereas regional metamorphism occurs in a wide area. Just so what are the main types of. The metamorphism comprises recrystallization metamorphic crystallization deformation fragmentation and.
2 Describe the effects on the surrounding rocks of an igneous intrusion that cooled in 500 years. What is the difference between low-grade and high-grade metamorphism. As the temperature andor pressure increases on a body of rock we say the rock undergoes prograde metamorphism or that the grade of metamorphism increases.
Volcanism on the other hand is the eruption of molten rocks hot gases or solidified rock fragments from an opening or vent in the earths crust. Weathering diagenesis and metamorphism are all changes that take place in solid rocks due to temperature pressure and fluid interactions. The grade of metamorphism generally increases with depth for the simple reason that both temperature and pressure factors become strong and stronger at deeper levels within the crust of the earth.
3 Explain why it is more difficult to know the pressure at which metamorphic rocks form than the temperature at which they form. The outcome of metamorphism depends on pressure temperature and the abundance of fluid involved and there are many settings with unique combinations of these factors. Retrograde metamorphism is normally produced by repeated regional metamorphism where a lower grade episode is superimposed on a higher grade one.
Contact metamorphism and regional. Most metamorphic rocks are the result of regional metamorphism also called dynamothermal metamorphism. There are two major kinds of metamorphism.
Starting in the chlorite zone near the Laphroaig whisky distillery on Islay perhaps bottle marked A rocks are slatey with well preserved sedimentary features. Metamorphosis is what butterflies do. In geology metamorphism is the formation of metamorphic rocks.
There are several different types of metamorphism including dynamic contact regional and retrogressive metamorphism that form and shape rocks. Metamorphism is the change that takes place within a body of rock as a result of it being subjected to high pressure andor high temperature.

10 4 Types Of Metamorphism And Where They Occur Physical Geology First University Of Saskatchewan Edition
Comments
Post a Comment